Imagine accessing your entire business infrastructure from anywhere, at any time, without the constraints of physical hardware. This dream has become a reality, unlocking a myriad of opportunities for organizations of all sizes.
Cloud computing is revolutionizing the way businesses operate, providing scalable resources and enhanced collaboration while drastically cutting costs.
With a shift towards a more agile and efficient model, companies are embracing this technology to improve operations, bolster security, and stay ahead of their competition.
The benefits, from disaster recovery to automated updates, are simply too significant to overlook.
In this essential guide, we will delve into the multifaceted benefits of cloud computing, exploring various service types, deployment models, and considerations to help you make informed decisions.
Whether you are a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding these elements will empower you to harness the true potential of the cloud and propel your business to new heights.
Table of Contents
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing on-demand computing resources via the Internet.
No longer tied to traditional on-premises IT infrastructure, enterprises can now leverage the unrivaled expertise and adaptability of cloud service providers. The myriad benefits of cloud computing make it indispensable for modern businesses.
Among the diverse types of cloud computing is Software as a Service (SaaS), which empowers users to access software applications online.
Cloud-based infrastructure offers unparalleled on-demand storage space and computing resources, reshaping how businesses approach IT solutions.
The advantages of cloud computing are manifold:
- Cost Savings: Minimize expenses by reducing the need for physical hardware.
- Security: Benefit from enhanced security measures provided by cloud providers.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Quickly adapt to changing business demands without overhauling systems.
- Rapid Deployment: Speed up the implementation of projects and services.
Perhaps the most compelling aspect of cloud technology is its exceptional accessibility. With a stable Internet connection, users can reach their data and applications from any device, promoting unparalleled operational efficiency.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is more than just a technology; it’s a catalyst for innovation and efficiency. By leveraging the power of remote servers and cloud platforms, businesses transcend traditional limitations—opening doors to new horizons of success.
As a pivotal enabler of modern enterprise solutions, cloud technology offers a wealth of benefits that cater to dynamic business needs while fostering growth, collaboration, and security.
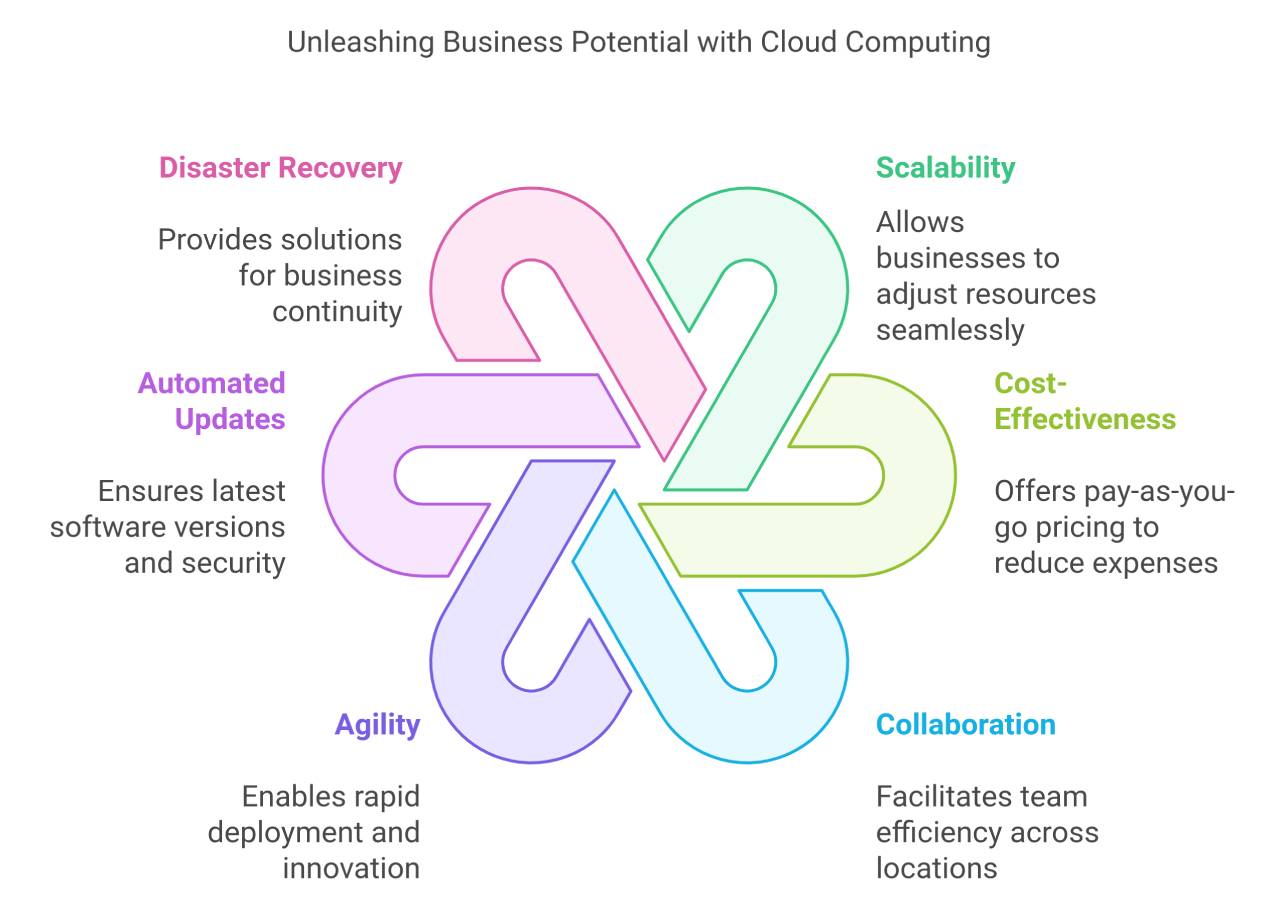
Scalable Resources for Growing Businesses
In today’s fast-paced business environment, growth and adaptability are crucial. Cloud environments offer the incredible benefit of infinite scalability, allowing businesses to adjust their bandwidth and computing resources seamlessly to meet fluctuating demands.
This capability ensures that your operations are never hindered by capacity limitations, promoting sustainable growth.
The hybrid cloud model further empowers organizations by leveraging public cloud resources when private cloud thresholds are reached, eliminating costly hardware investments.
This agility in operational responses to market changes is a game-changer for businesses striving to maintain their competitive edge.
Cost-Effectiveness through Pay-as-You-Go Models
One of the most attractive advantages of cloud computing is its cost-effectiveness, primarily through the pay-as-you-go pricing model. This approach allows businesses to pay only for the cloud services and storage space they genuinely use.
Gone are the days of overpaying for underutilized resources. Reduced maintenance costs and easy access to essential data further cut down on expenses.
In fact, a survey by Bitglass revealed that half of all CIOs and IT leaders experienced cost savings due to cloud-based applications as early as 2015.
This adaptable payment structure not only slashes costs but also streamlines budget management for IT resources.
Enhanced Collaboration and Accessibility
Collaboration is at the heart of innovation, and cloud computing facilitates this by offering robust data sharing and real-time editing capabilities.
This enhances team efficiency across geographies, enabling employees to work together effectively regardless of physical location.
Role-based access controls ensure that collaboration does not compromise security, allowing authorized personnel only to access sensitive data.
Cloud platforms support synchronous operations among different teams, maintaining the visibility of their actions—a vital component for modern, flexible work environments.
Employers can coordinate and supervise remote and in-office staff on the same projects, ensuring a unified, collaborative approach.
Improved Agility and Speed of Deployment
Cloud computing shines here with its ability to deploy applications rapidly, eliminating the painstaking process of configuring servers or waiting for hardware procurement.
Developers can spin up new computing instances in seconds, facilitating faster software development and innovation.
This capability enables continuous integration and delivery, leading to frequent releases of new features and improvements.
The cloud also offers instant access to collected data, enhancing decision-making processes and enabling swift organizational response to changing business needs.
Automated Updates and Maintenance
Say goodbye to routine IT maintenance and time-consuming updates. Cloud-based software ensures that businesses always have the latest software versions and security patches through automated updates.
This not only frees personnel from mundane tasks but also enhances system reliability and performance.
With continuous connection to the Internet, cloud services facilitate ongoing improvements and security enhancements, reducing the need for external IT consultations.
Automated management ensures resources and infrastructure devices remain up-to-date without manual interventions, allowing teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Robust Disaster Recovery Solutions
In a world fraught with unpredictability, robust disaster recovery solutions provided by cloud-based services are indispensable.
By deploying services across multiple data centers, cloud environments guarantee uninterrupted operations even if one server faces downtime.
This resilience ensures business continuity during emergencies such as natural disasters or power outages.
Organizations can swiftly recover data, facilitated by extensive cloud storage options that support backup recovery and version rollback.
In a multi-cloud setup, redundancy reduces downtime risks further, protecting data from malware, corruption, and other disruptions.
Data Security Measures in Cloud Solutions
Security is paramount in any digital landscape, and cloud providers rise to the challenge with advanced measures like authentication, access control, and encryption.
By implementing granular permissions and multi-factor authentication, they decrease potential security vulnerabilities and safeguard sensitive data.
Regular audits by software vendors reinforce the trust in data safety, while the ability to back up information to the cloud mitigates risks of loss due to hardware failures.
Cloud-based systems allow for real-time monitoring, offering oversight that enhances data protection and counters threats like data theft, ensuring a secure environment for critical business operations.
Cloud computing isn’t just the future—it’s an essential part of the present, providing unprecedented advantages that are transforming the business landscape. Embrace the cloud and unleash the full potential of your enterprise!
Types of Cloud Computing Services
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, understanding the types of cloud computing services is crucial for businesses aiming to harness the full power of cloud technology.
At the forefront, we have three primary categories that enable organizations to meet their unique business demands and drive innovation like never before: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
Each service offers varying degrees of control, flexibility, and opportunity for dynamic business growth, wrapped in a secure and scalable cloud environment.
Let’s dive into the passionate universe of these cloud-based services and explore the myriad benefits they bring.
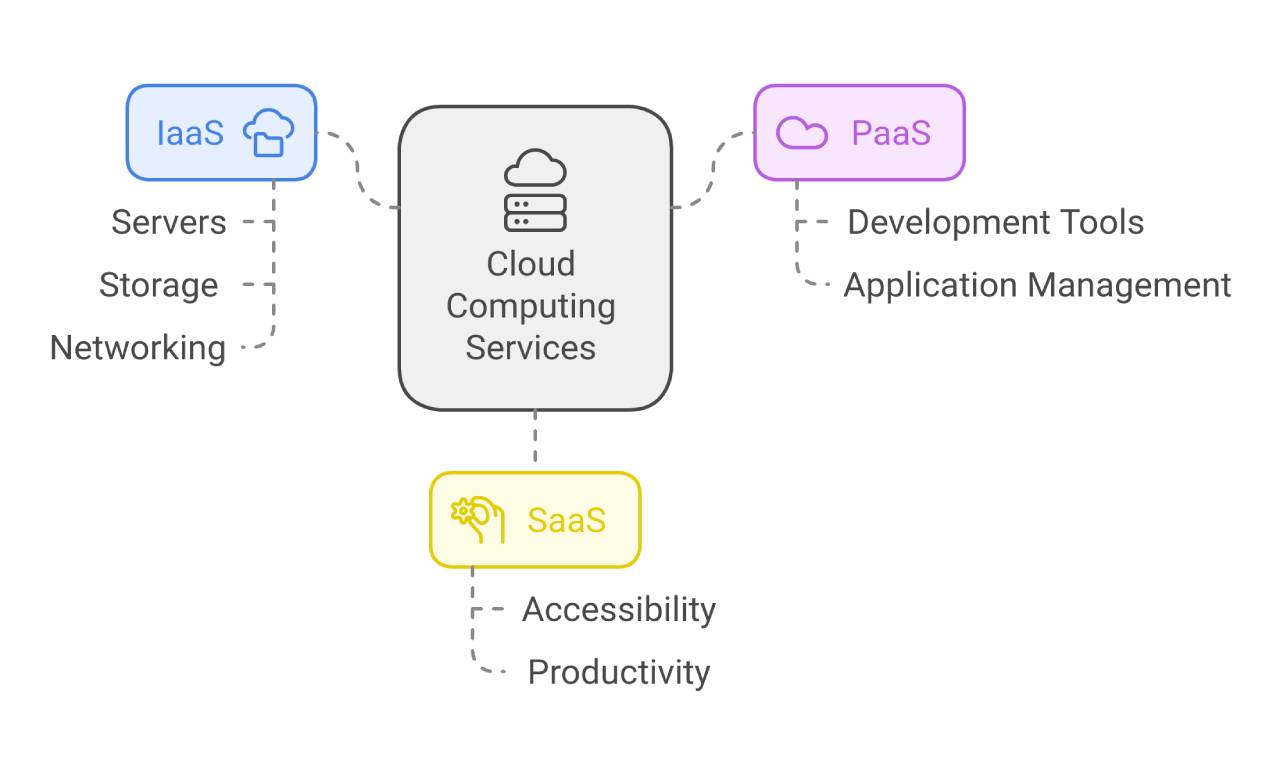
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a revolution in the domain of IT infrastructure, presenting businesses with access to essential computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking, all available over the internet.
This form of cloud computing service empowers organizations to craft bespoke business solutions without the financial burden of maintaining physical infrastructure.
Consider that with IaaS, businesses like those using Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure not only minimize their IT expenses but also relieve their IT staff from mundane maintenance tasks, thus unleashing their creative potential.
With IaaS, control remains firmly in the hands of users, who can configure storage, choose operating systems, and deploy applications, while the cloud service provider manages the underlying infrastructure.
This pay-as-you-go model ensures that companies can flexibly scale and customize their resources as per their specific needs, mimicking traditional on-site setups yet with unparalleled convenience and agility.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Imagine a development environment that erases the complexities of configuring hardware and managing underlying infrastructure—this is the essence of Platform as a Service (PaaS).
It offers an on-demand framework for developing, testing, managing, and delivering robust software applications, simplifying the journey of crafting web and mobile apps.
By utilizing PaaS solutions like AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, or Microsoft Azure, developers and startups alike benefit from essential tools and infrastructure tailored for building cloud-based applications.
The pay-as-you-go model not only ensures economic efficiency but also provides developers the flexibility to focus solely on their innovative outputs without the anxiety of backend maintenance. With PaaS, the stage is set for creativity, unleashing a world where ideas transform seamlessly into applications.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) stands as a beacon of simplicity and accessibility in the world of software applications.
By delivering fully functional software over the internet, it absolves enterprises of the need for cumbersome local installations.
This model, often termed hosted or on-demand software, sees the cloud service provider orchestrating everything from hardware to software security, making IT management an absolute breeze for users.
Through SaaS, businesses achieve unprecedented levels of productivity and accessibility. This is particularly advantageous in today’s remote work environments, providing seamless access to applications regardless of geographical location.
By circumventing upfront infrastructure expenditures, SaaS emerges as a cost-effective solution, harmonizing enhanced efficiency with economic prudence.
These cloud-based software applications allow businesses to focus on what truly matters—innovation and growth, unfettered by technological constraints.
Different Deployment Models
Cloud computing has revolutionized how organizations operate, providing three primary deployment models—public, private, and hybrid—that cater to diverse business needs and capacities.
These models are crafted to meet the varying demands of modern enterprises, offering unique advantages and flexibilities.
Public Cloud Benefits and Considerations
Public clouds stand as beacons of accessibility and efficiency in the cloud environment, operated by third-party service providers that deliver resources such as storage space and servers over the Internet.
This arrangement removes the need for businesses to invest heavily in underlying infrastructure, thereby slashing costs associated with hardware procurement and maintenance.
The scalable RAM and flexible bandwidth in public clouds ensure that enterprises can adjust their storage and processing needs quickly to meet fluctuating demands.
Furthermore, public clouds break the chains of location by offering broad accessibility, allowing users and organizations to access computing services from any device with an Internet connection. This mobility and flexibility empower businesses to meet operational needs quickly and efficiently.
Private Cloud Advantages for Security
Private clouds are the champions of data security and control, providing businesses a fortified environment to manage and store their sensitive information.
Unlike public models, private clouds are dedicated to a single organization, leveraging internal hosting and company firewalls to safeguard data from third-party providers.
This exclusivity not only reduces the risk of data breaches but also allows organizations greater control over their data security practices.
With private clouds, businesses benefit from customizable security measures tailored to comply with strict data protection regulations, providing peace of mind and safeguarding sensitive information.
Hybrid Cloud for Flexibility
A hybrid cloud architecture emerges as a versatile solution, skillfully combining public, private, and on-premises infrastructure to create a seamless and adaptable computing environment.
This model offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing organizations to rapidly provision resources and transition workloads between clouds based on changing computing and cost requirements.
By harnessing the power of both public and private clouds, businesses can scale their on-premises infrastructure effortlessly during peak demand periods without the burden of maintaining excess resources.
This scalability ensures financial efficiency, as organizations pay only for the temporary resources they utilize, optimizing their cost structures.
Multi-Cloud Strategy for Vendor Diversification
In an era where vendor lock-in and service outages can cripple operations, a multi-cloud strategy offers businesses a lifeline of resilience and flexibility.
By deploying multiple Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) providers, companies can operate or migrate applications across various cloud platforms, effectively minimizing reliance on a single cloud provider.
This strategy not only reduces the risk of service interruptions but allows enterprises to leverage competitive pricing and tailor cloud usage based on specific technical and budget requirements.
As cloud providers continue to standardize services and APIs, the transition to a multi-cloud environment becomes increasingly manageable, fostering innovation and flexibility in application development across diverse cloud platforms.
By understanding and strategically utilizing these deployment models, businesses can maximize the benefits of cloud computing, driving innovation, flexibility, and resilience amidst evolving business demands.
Challenges and Considerations
Embracing cloud-based software solutions offers transformative potential for businesses ready to innovate, scale, and respond to rapid market changes.
Yet, as with any technological advancement, there are challenges and considerations that must be addressed to harness the full benefits of cloud computing. Let’s explore these considerations in detail.
Security Concerns in Cloud Environments
Security in cloud environments remains a paramount concern for organizations venturing into cloud computing. The inherent risks such as data breaches, hacking of APIs, and compromised credentials are significant.
A major challenge is the often perceived lack of transparency in handling sensitive data within the cloud. Despite the robust security measures promised by cloud service providers, businesses must meticulously manage their cloud configurations and develop stringent business policies.
This includes vigilance against internal threats from employees and ensuring a clear understanding of shared security responsibilities between the organization and the providers. Fortunately, cloud service providers, with their dedicated focus on security, often offer more comprehensive protection compared to traditional in-house IT systems.
Potential Vendor Lock-In Risks
One of the most daunting aspects of cloud computing is the risk of vendor lock-in. Once systems migrate to a cloud provider’s platform, disentangling can be challenging due to the integration of cloud services with core business processes.
This concern is exacerbated by a loss of control over the cloud infrastructure managed by third-party vendors. Vendor lock-in can tie organizations to a specific provider, making it difficult to switch without significant disruptions or cost.
However, by adopting multi-cloud environments, businesses can strategically mitigate this risk and reduce reliance on a single cloud provider. This approach allows for greater flexibility and maintains the integrity of business continuity.
Compliance and Regulatory Issues
The transition to cloud storage presents unique compliance and regulatory challenges. Moving data from on-premises to the cloud, overseen by a third-party, complicates adherence to industry regulations.
Organizations must remain vigilant about where their data resides to ensure regulatory compliance and uphold business governance.
This involves navigating various regulatory requirements associated with external cloud services and understanding the implications for IT compliance, data quality, and risk management.
Decentralized control over provisioning and infrastructure operation management can complicate proper IT governance; hence, organizations need robust strategies in place to manage these compliance issues during cloud migration.
Downtime and Reliability Concerns
The reliability advantages in cloud computing cannot be overstated, but the possibility of downtime remains a critical concern.
Despite the cloud’s capability to simplify data backup, disaster recovery, and business continuity, unexpected outages can impact productivity, brand reputation, and revenue.
Thankfully, cloud-based services excel in disaster recovery—organizations can recover data swiftly, often within four hours, compared to longer recovery times for non-cloud users.
Regular updates and maintenance by cloud providers further mitigate outage risks, ensuring data is consistently backed up across multiple redundant sites.
This centralized backup system reduces the risk of data loss and enhances overall reliability, safeguarding critical information in times of crisis.
Tips for Maximizing Cloud Computing Benefits
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, cloud-based software is not just a convenience—it’s a transformative force.
The advantages of cloud computing are manifold, and when leveraged correctly, they can propel businesses to new heights of operational excellence and innovation.
From substantial cost savings to enhanced accessibility and sustainability, the cloud is pivotal in shaping the future of business technology.
Let’s delve into how you can unlock the full potential of cloud environments and elevate your organizational capabilities.
Conducting a Needs Assessment
Embarking on the cloud journey begins with understanding your organization’s specific needs. Cloud computing provides a flexible, pay-as-you-go pricing model that aligns with your operational demand, cutting down unnecessary expenses.
As you assess your requirements, consider how cloud storage and remote servers can fortify your disaster recovery plans—ensuring that your data and applications remain safe even if local systems fail.
Additionally, the mobility offered by cloud services lets your team access vital systems from anywhere, fostering real-time collaboration regardless of their geographical location.
Key Considerations:
- Cost-Efficiency: Pay only for the services you use.
- Scalability: Adapt quickly to changing business demands.
- Disaster Recovery: Benefit from robust, remote solutions.
- Accessibility: Ensure seamless data access across the globe.
Choosing the Right Cloud Solutions
Selecting the right cloud service provider is crucial for maximizing cloud benefits. Prioritize providers that balance reliability with advanced security features, catering specifically to your organizational needs.
The physical location of cloud providers’ servers is also vital when dealing with sensitive data, helping mitigate privacy concerns. By embracing a hybrid cloud or multicloud approach, businesses can achieve a balance in computational power and flexibility.
This allows for integration and customization of cloud applications, thus quickly adapting technologies to your specific operational demands.
Key Considerations:
- Reliability & Security: Ensure high uptime and data protection.
- Hybrid & Multicloud Models: Balance cost-efficiency and processing power.
Regularly Reviewing Cloud Spending
To truly reap the benefits of cloud computing, continuous financial oversight is essential. It’s common for organizations to waste a significant portion of their cloud budget—up to 30%—due to unchecked spending.
Regular reviews help identify unnecessary expenses and optimize cost strategies. With over one-third of businesses facing substantial budget overruns, monitoring emerging cloud platforms and adjusting spending practices are crucial to prevent excesses.
Remember, maintaining control over your cloud budget requires not just technology but a strategic approach.
Strategies for Cost Management:
- Routine Financial Evaluations: Aim to uncover inefficiencies.
- Dedicated Optimization Tools: Utilize technology to track and control spending.
- Strategic Adjustments: Stay agile with your financial plans.
Training Teams on Best Practices
Educating your team on cloud best practices is a cornerstone for successful adoption and sustained productivity.
Cloud environments break down barriers to collaboration, allowing cross-functional teams to work simultaneously on shared infrastructures without conflicts.
Regular role-based access controls ensure data security while enabling effective teamwork. With ongoing updates from cloud service providers, your team remains equipped with the latest tools, driving continuous improvement in all facets of collaboration and productivity.
Training Tips:
- Foster Role-Based Access Security: Protect sensitive information.
- Embrace Continual Learning: Keep up with updates and new features.
- Encourage Cross-Functional Collaboration: Leverage diverse team strengths for innovation.
Enthusiastically harness the power of cloud technology, and watch as your organization flourishes with enhanced efficiency, security, and growth potential—transforming not just how you do business, but how you envision the future.
Conclusion
The transformative power of cloud-based software is undeniable. Its ability to adapt swiftly to business demands ensures seamless continuity even amidst natural disasters.
With the support of robust cloud infrastructure, businesses can rely on a third-party provider to safeguard their data and operations. Cloud providers offer a variety of service models, from public, private to hybrid cloud environments, catering to diverse needs and preferences.
The core advantages of cloud computing include enhanced scalability, marked by its capacity to meet varying storage space requirements, and impressive flexibility.
Cloud platforms offload the burden of managing underlying infrastructure, allowing businesses to focus on growth and innovation. Operating systems and software applications find a resilient home on remote servers, ensuring smooth operations even in the face of adversity.
Moreover, the integration of disaster recovery strategies bolsters business continuity plans, with cloud servers ensuring data accessibility and recovery. Internet connectivity becomes the lifeline, enabling access to cloud services from anywhere at any time.
Harnessing the power and versatility of cloud technology, businesses today stand stronger and more agile, meeting future challenges with confidence and efficiency.
The cloud is not just a technological advancement—it’s a transformational leap into a more secure, intelligent, and responsive era of computing.