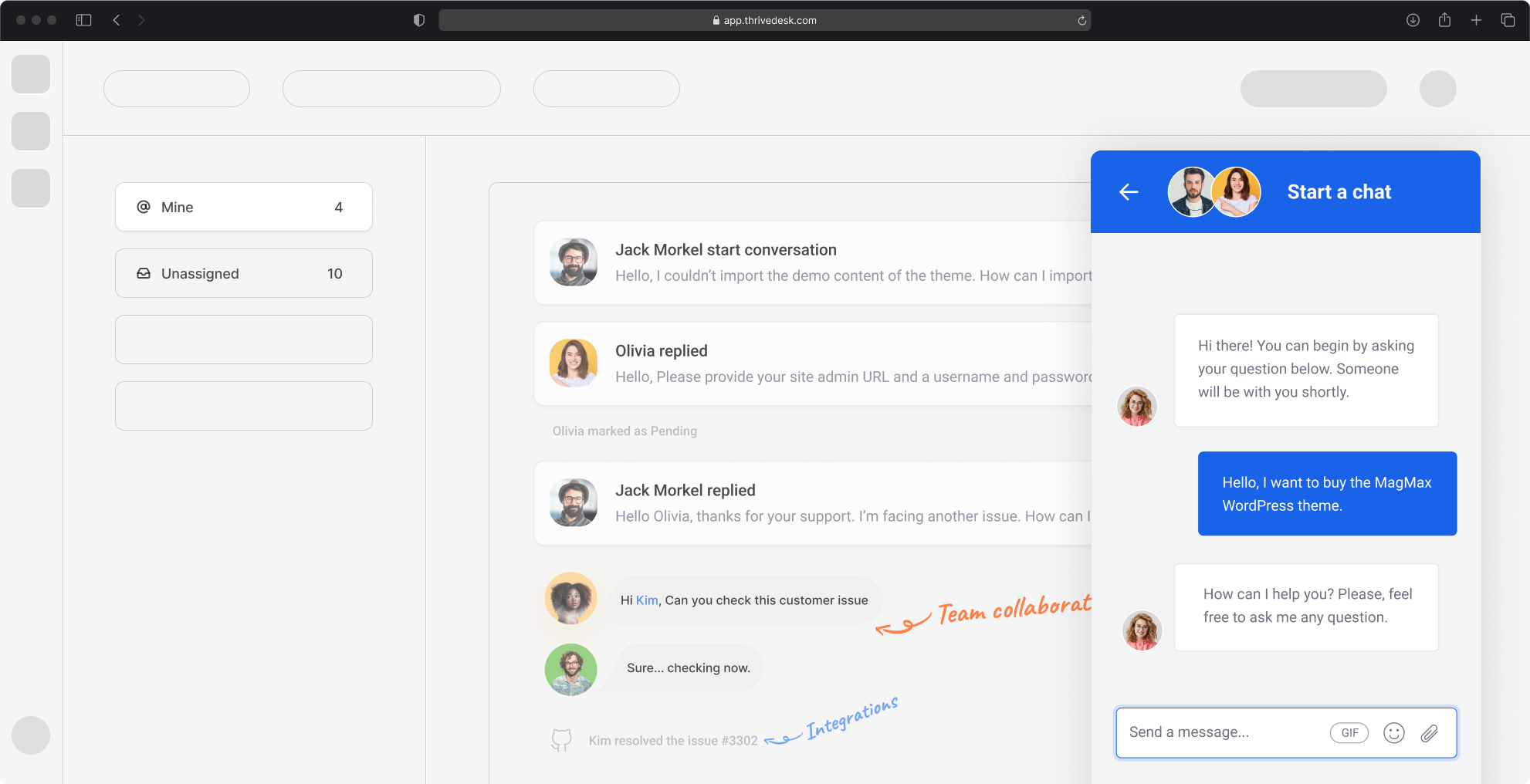
Los buzones de correo compartidos pueden ser un arma de doble filo. Agilizan la comunicación entre equipos y departamentos, actuando como un centro neurálgico para consultas, solicitudes y tareas. Pero sin una gestión adecuada, este espacio compartido puede volverse caótico rápidamente.
Imagínese una bandeja de entrada desordenada y repleta de correos electrónicos sin respuesta: esa es la posible desventaja de los buzones de correo compartidos.
Esta guía le permitirá aprovechar los buzones compartidos de manera eficaz, manteniendo a su equipo informado y evitando fallas en la comunicación.
¿Qué es un buzón compartido?
Un buzón compartido es una bandeja de entrada de correo electrónico a la que pueden acceder y administrar de forma colectiva varios usuarios. Permite que los miembros del equipo colaboren en las comunicaciones por correo electrónico, generalmente para fines departamentales o funcionales, como atención al cliente o consultas de ventas.
Los buzones de correo compartidos ofrecen varias ventajas, como una mayor eficiencia del equipo, una comunicación centralizada y un flujo de trabajo optimizado. Permiten que varios miembros del equipo envíen y reciban correos electrónicos desde una única dirección, lo que garantiza respuestas coherentes y reduce el riesgo de perder mensajes. Esta configuración es especialmente útil para gestionar tickets de soporte de gran volumen o cuando se necesita continuidad en los cambios de turno o las ausencias de los empleados.
Todas las solicitudes de los clientes en un solo lugar
Tanto si maneja grandes volúmenes de correo electrónico como si sólo busca mejorar la comunicación en equipo, ThriveDesk puede ayudarle a mantenerse organizado y al día en su trabajo.
10 prácticas recomendadas para el buzón compartido
1. Establecer permisos de acceso claros
Una de las mejores prácticas fundamentales para la gestión de buzones compartidos es establecer permisos de acceso claros. Un buzón compartido, por su propia naturaleza, implica que varios usuarios accedan e interactúen con la misma cuenta de correo electrónico. Si no se implementan los controles de acceso adecuados, pueden producirse confusiones, duplicaciones de esfuerzos e incluso violaciones de seguridad.
Defina y asigne roles y permisos específicos a cada usuario o grupo para garantizar el buen funcionamiento de un buzón compartido.
Estos permisos deben basarse en las responsabilidades, tareas y nivel de participación de cada individuo en el buzón compartido. De esta manera, las organizaciones pueden mantener el control sobre quién puede ver, enviar o administrar correos electrónicos dentro del buzón compartido, lo que evita el acceso no autorizado o el manejo indebido accidental de información confidencial.
Los permisos de acceso normalmente se pueden establecer en varios niveles, como:
- Acceso completo: Este nivel de permiso otorga a los usuarios la capacidad de leer, enviar y administrar correos electrónicos dentro del buzón compartido y modificar los permisos de acceso de otros usuarios.
- Enviar como: Los usuarios con este permiso pueden enviar correos electrónicos desde el buzón compartido, pero no pueden leer ni administrar correos electrónicos existentes.
- Solo lectura: Como sugiere el nombre, este nivel de permiso permite a los usuarios ver y leer correos electrónicos dentro del buzón compartido, pero no les otorga la capacidad de enviar o administrar correos electrónicos.
Las organizaciones pueden lograr el equilibrio adecuado entre colaboración y control asignando cuidadosamente estos permisos en función de los roles y responsabilidades.
Por ejemplo, los representantes de atención al cliente pueden necesitar acceso completo a la soporte@empresa.com buzón de correo para gestionar las consultas de forma eficaz. Al mismo tiempo, los miembros del equipo de marketing pueden necesitar únicamente permisos de "enviar como" para enviar correos electrónicos promocionales desde el buzón de correo compartido.
También es fundamental revisar y actualizar periódicamente estos permisos a medida que los miembros del equipo se incorporan, abandonan o cambian de función dentro de la organización. No hacerlo puede dar lugar a accesos no autorizados o a la exposición de información confidencial.
La implementación de permisos de acceso claros para buzones compartidos mejora la seguridad y el control y promueve la responsabilidad y la propiedad entre los miembros del equipo.
Al garantizar que cada usuario tenga el nivel de acceso adecuado, las organizaciones pueden agilizar la comunicación, reducir el riesgo de errores y mantener un entorno de buzón compartido bien organizado y eficiente.
2. Implementar convenciones de nombres
Implementar una convención de nomenclatura clara y consistente es crucial para mantener la organización y la eficiencia en un entorno de buzón compartido, donde múltiples usuarios acceden e interactúan con correos electrónicos.
Sin un sistema de nombres estandarizado, identificar y localizar correos electrónicos específicos se vuelve cada vez más difícil, lo que genera confusión, duplicación de esfuerzos y posible falta de comunicación.
Establecer una convención de nomenclatura bien definida para los correos electrónicos dentro de un buzón compartido proporciona numerosos beneficios, entre ellos:
- Fácil identificación: Una convención de nombres clara y descriptiva permite a los usuarios identificar rápidamente el asunto y el propósito de un correo electrónico, lo que reduce la necesidad de abrir y leer varios mensajes.
- Capacidad de búsqueda mejorada: Al incorporar palabras clave o códigos relevantes en la línea de asunto del correo electrónico, los usuarios pueden buscar y filtrar fácilmente en el buzón compartido, ahorrando tiempo y esfuerzo.
- Organización mejorada: Una convención de nombres consistente ayuda a agrupar correos electrónicos relacionados, lo que facilita la gestión y priorización de tareas o proyectos.
- Colaboración y contexto: Los nombres de correo electrónico descriptivos brindan contexto e información de fondo a los miembros del equipo, lo que facilita una mejor colaboración y comprensión.
Al implementar una convención de nombres para un buzón compartido, tenga en cuenta las siguientes prácticas recomendadas:
- Utilice un formato estandarizado: Establezca un formato consistente para las líneas de asunto de los correos electrónicos, como “[NOMBRE DEL PROYECTO] – [BREVE DESCRIPCIÓN]” o “[TICKET #] – [ASUNTO]”.
- Incorporar metadatos relevantes: Incluya información de identificación como nombres de proyectos, nombres de clientes, números de tickets o rangos de fechas en la línea de asunto para brindar un contexto valioso.
- Sea conciso y descriptivo: Al incorporar detalles relevantes, intente utilizar líneas de asunto concisas y descriptivas para garantizar la claridad y la legibilidad.
- Evite la ambigüedad: Evite líneas de asunto vagas o genéricas que puedan causar confusión o malinterpretación.
- Documentar y comunicar: Documente claramente la convención de nomenclatura y proporcione capacitación o pautas para garantizar una adopción consistente en todo el equipo.
Establecer un proceso para revisar y actualizar periódicamente la convención de nombres es igualmente importante a medida que evolucionan las necesidades o los proyectos del equipo. Involucrar a las partes interesadas y recopilar comentarios puede ayudar a refinar y optimizar el sistema de nombres para lograr la máxima eficiencia.
Las organizaciones pueden mejorar significativamente la gestión del correo electrónico, mejorar la colaboración y optimizar los flujos de trabajo mediante la implementación de una convención de nombres bien diseñada para los buzones de correo compartidos. Esta práctica simple pero eficaz puede transformar un buzón de correo compartido desordenado y abarrotado en un centro de comunicación altamente eficiente y productivo.
3. Establecer y comunicar pautas de uso
Si bien los buzones compartidos están diseñados para facilitar la colaboración y agilizar la comunicación, su eficacia depende en gran medida de la implementación constante de pautas de uso claras.
Los buzones compartidos pueden desorganizarse rápidamente sin un conjunto de reglas y protocolos acordados, lo que genera mensajes perdidos, esfuerzos duplicados y posible falta de comunicación.
Establecer y comunicar pautas de uso integrales es fundamental para garantizar que todos los miembros del equipo estén en la misma sintonía a la hora de administrar y responder correos electrónicos dentro del buzón compartido. Estas pautas deben cubrir varios aspectos del uso del buzón compartido, entre ellos:

Todas las solicitudes de los clientes en un solo lugar
Tanto si maneja grandes volúmenes de correo electrónico como si sólo busca mejorar la comunicación en equipo, ThriveDesk puede ayudarle a mantenerse organizado y al día en su trabajo.
Gestión de la bandeja de entrada:
- Especifique cómo deben manejarse los mensajes entrantes, como asignar propiedad, categorizar o escalar consultas urgentes.
- Determinar protocolos para marcar mensajes como leídos, no leídos o que requieren seguimiento.
- Establecer pautas para archivar o eliminar mensajes después de haber sido abordados.
Protocolos de respuesta:
- Definir plazos y prioridades de respuesta en función de la naturaleza o urgencia de la consulta.
- Proporcionar plantillas o pautas para elaborar respuestas profesionales y consistentes.
- Aclarar cuándo es apropiado reenviar o delegar mensajes a miembros o departamentos específicos del equipo.
Delegación de tareas y seguimiento:
- Describir los procedimientos para asignar tareas o acciones de seguimiento dentro del buzón compartido.
- Determinar cómo se deben rastrear y monitorear las tareas para garantizar su finalización oportuna.
- Establecer procesos de escalamiento para tareas vencidas o problemas no resueltos.
Acceso y seguridad:
- Reforzar la importancia de respetar los permisos de acceso y evitar el intercambio no autorizado de credenciales de inicio de sesión.
- Proporcionar orientación sobre el manejo de información sensible o confidencial dentro del buzón compartido.
- Enfatizar la necesidad de mantener una comunicación profesional y adherirse a las políticas y regulaciones organizacionales.
Comunicar eficazmente estas pautas de uso es tan importante como establecerlas. Considere las siguientes estrategias:
- Documentación: Desarrollar un manual o guía integral para buzones compartidos que describa todas las pautas y protocolos en detalle.
- Capacitación: Realice sesiones de capacitación o talleres periódicos para garantizar que todos los miembros del equipo, incluidos los nuevos empleados, estén familiarizados con las pautas de uso.
- Recordatorios regulares: Envíe recordatorios periódicos por correo electrónico o incorpore las mejores prácticas de buzón compartido en reuniones o comunicaciones de equipo.
- Predicar con el ejemplo: Incentive a los gerentes y líderes de equipo a modelar y reforzar las pautas de uso a través de sus propias acciones y comportamientos.
Al establecer y comunicar de manera consistente pautas de uso claras, las organizaciones pueden garantizar que sus buzones compartidos permanezcan organizados, eficientes y alineados con los objetivos y estándares de la organización.
Este enfoque proactivo agiliza la comunicación y fomenta la responsabilidad, el profesionalismo y una cultura de equipo colaborativo.
4. Limpie y organice periódicamente el buzón
Incluso con permisos de acceso claros, convenciones de nombres y pautas de uso establecidas, los buzones compartidos pueden desordenarse y volverse desordenados rápidamente si no se mantienen con regularidad. Una bandeja de entrada o una estructura de carpetas abarrotadas pueden afectar la productividad, dificultar la localización de información importante y aumentar el riesgo de perder comunicaciones críticas.
Implementar un proceso regular de limpieza y organización es crucial para garantizar que los buzones compartidos sigan siendo eficientes y efectivos.
Esta práctica recomendada implica un enfoque sistemático para ordenar, archivar y eliminar correos electrónicos, así como para mantener una estructura de carpetas organizada. Al hacerlo, las organizaciones pueden obtener numerosos beneficios, entre ellos:
- Visibilidad y accesibilidad mejoradas: Un buzón compartido bien organizado facilita la localización de correos electrónicos o hilos específicos, lo que reduce el tiempo dedicado a la búsqueda y aumenta la productividad general.
- Colaboración mejorada: La colaboración y el intercambio de conocimientos se facilitan cuando los miembros del equipo pueden encontrar y consultar rápidamente información relevante dentro del buzón compartido.
- Reducción del desorden y la confusión: La limpieza y organización periódicas ayudan a evitar la acumulación de correos electrónicos innecesarios u obsoletos, minimizando distracciones y posibles malentendidos.
- Mejor gestión del almacenamiento: Al archivar o eliminar correos electrónicos obsoletos, las organizaciones pueden optimizar su almacenamiento de correo electrónico y garantizar un rendimiento eficiente.
Para limpiar y organizar eficazmente un buzón compartido, tenga en cuenta las siguientes prácticas recomendadas:
- Establecer una estructura de carpetas consistente: Cree una jerarquía de carpetas lógica e intuitiva basada en proyectos, clientes o temas, lo que facilita la categorización y localización de correos electrónicos.
- Implementar un programa de limpieza regular: Reserve intervalos de tiempo específicos (por ejemplo, semanales o mensuales) para revisar y limpiar el buzón compartido, asegurándose de que permanezca organizado y sin desorden.
- Definir políticas de retención: Establecer pautas claras sobre cuánto tiempo deben conservarse los correos electrónicos en el buzón compartido antes de archivarse o eliminarse, teniendo en cuenta los requisitos legales, de cumplimiento y operativos.
- Aproveche las herramientas de automatización: Utilice filtros de correo electrónico, reglas y herramientas de automatización para ordenar y organizar automáticamente los mensajes entrantes, lo que reduce el esfuerzo manual y garantiza la coherencia.
- Involucre a todo el equipo: Anime a todos los miembros del equipo que acceden al buzón compartido a contribuir al proceso de limpieza y organización, fomentando un sentido de pertenencia y responsabilidad.
- Proporcionar capacitación y apoyo: Ofrecer sesiones de capacitación o recursos para garantizar que todos los miembros del equipo comprendan y sigan los protocolos de limpieza y organización establecidos.
Al priorizar la limpieza y la organización regulares, las organizaciones pueden transformar sus buzones compartidos en centros de colaboración eficientes y productivos.
Esta práctica recomendada mejora la productividad general y contribuye a un entorno de comunicación más organizado y profesional, lo que en última instancia beneficia tanto a los equipos internos como a las partes interesadas externas.
5. Configurar reglas y filtros automatizados
Los buzones compartidos pueden verse rápidamente inundados por un gran volumen de mensajes entrantes, lo que hace que la clasificación y organización manual sea una tarea abrumadora. Implementar reglas y filtros automatizados es una práctica recomendada eficaz para optimizar la gestión de buzones compartidos y mejorar la eficiencia.
Las reglas y filtros automatizados son instrucciones predefinidas que automáticamente clasifican, categorizan o toman acciones específicas en los correos electrónicos entrantes según criterios predeterminados.
Al aprovechar esta funcionalidad, las organizaciones pueden reducir significativamente el tiempo y el esfuerzo necesarios para administrar buzones compartidos y, al mismo tiempo, garantizar un procesamiento de mensajes consistente y preciso.
A continuación se muestran algunos ejemplos de cómo se pueden utilizar eficazmente las reglas y los filtros automatizados en buzones compartidos:
- Enrutamiento de mensajes: Configure reglas para enrutar automáticamente los correos electrónicos entrantes a carpetas específicas o a miembros del equipo según palabras clave, remitentes o líneas de asunto. Esto garantiza que los mensajes se dirijan rápidamente a las personas o proyectos adecuados, lo que minimiza los retrasos y los posibles descuidos.
- Marcado de prioridad: Configure filtros para marcar o resaltar automáticamente correos electrónicos con determinadas palabras clave o remitentes, identificando fácilmente mensajes de alta prioridad o urgentes.
- Respuestas automáticas: Cree reglas para enviar mensajes de respuesta automática a remitentes específicos o para tipos específicos de consultas, proporcionando un reconocimiento inmediato y estableciendo expectativas para los tiempos de respuesta.
- Filtrado de spam y correo basura: Implemente filtros para identificar y mover automáticamente correos electrónicos sospechosos de ser spam o basura a una carpeta designada, lo que reduce el desorden en el buzón compartido y mejora la organización general.
- Archivado y conservación: Configure reglas para archivar o mover automáticamente correos electrónicos antiguos a carpetas o ubicaciones de almacenamiento designadas. Esto garantiza el cumplimiento de las políticas de retención y, al mismo tiempo, mantiene el buzón compartido organizado y manejable.
Al implementar reglas y filtros automatizados, es fundamental planificarlos y probarlos cuidadosamente para garantizar que funcionen de manera precisa y deseada. Tenga en cuenta las siguientes prácticas recomendadas:
- Involucrar a las partes interesadas: Colabore con los miembros del equipo que utilizan el buzón compartido para recopilar información y requisitos para reglas y filtros automatizados.
- Empiece por algo sencillo: Comience con reglas y filtros básicos, introduciendo gradualmente configuraciones más avanzadas según sea necesario, asegurando una transición fluida y minimizando posibles interrupciones.
- Documentar y compartir: Documente las reglas y los filtros implementados y comparta esta información con todos los miembros del equipo para garantizar la transparencia y una comprensión consistente.
- Revise y actualice periódicamente: Revise y actualice periódicamente las reglas y los filtros automatizados para garantizar que se alineen con las necesidades comerciales cambiantes y los patrones de correo electrónico.
Al aprovechar el poder de las reglas y filtros automatizados, las organizaciones pueden agilizar significativamente la gestión de buzones compartidos, reduciendo el esfuerzo manual y minimizando el riesgo de comunicaciones perdidas o retrasadas.
Esta práctica recomendada no solo mejora la productividad, sino que también contribuye a un flujo de trabajo más organizado y eficiente, lo que permite a los equipos centrarse en tareas de mayor valor y generar mejores resultados comerciales generales.
6. Implemente una etiqueta de correo electrónico adecuada
Si bien los buzones de correo compartidos están diseñados para facilitar la colaboración y la comunicación, su eficacia puede verse afectada por prácticas de correo electrónico inadecuadas o poco profesionales.
Implementar y cumplir con una etiqueta de correo electrónico adecuada es una práctica recomendada crucial que no solo garantiza una experiencia positiva para los destinatarios, sino que también fomenta un entorno de buzón compartido profesional y organizado.
La etiqueta del correo electrónico comprende un conjunto de pautas y prácticas recomendadas para redactar, enviar y responder correos electrónicos de manera profesional y cortés. En el contexto de los buzones compartidos, donde varios miembros del equipo pueden interactuar con los mismos correos electrónicos, seguir la etiqueta adecuada se vuelve aún más importante para mantener la coherencia, la claridad y el profesionalismo.
A continuación se presentan algunos aspectos clave de la etiqueta del correo electrónico que se deben tener en cuenta para los buzones compartidos:
- Líneas de asunto claras y concisas: Utilice líneas de asunto descriptivas y relevantes que reflejen con precisión el contenido del correo electrónico, lo que facilita que los destinatarios y los miembros del equipo identifiquen y prioricen los mensajes.
- Tono y lenguaje profesional: Mantenga un tono cortés, respetuoso y profesional en todas las comunicaciones por correo electrónico, evitando un lenguaje demasiado casual o informal que pueda percibirse como poco profesional.
- Formato y estructura adecuados: Utilice técnicas de formato adecuadas, como encabezados claros, viñetas y saltos de párrafo, para mejorar la legibilidad y garantizar que la información importante sea fácilmente identificable.
- Saludos y despedidas apropiados: Utilice saludos y cierres apropiados que se alineen con el nivel de formalidad requerido para la comunicación específica, asegurando un tono consistente y profesional en todo momento.
- Revisar antes de enviar: Revise cuidadosamente los correos electrónicos para verificar la ortografía, la gramática y la precisión antes de enviarlos para evitar errores o malentendidos, que pueden dar una mala imagen de la organización.
- Responda con prontitud: Establecer y cumplir plazos de respuesta razonables para garantizar que las consultas o solicitudes se atiendan de manera oportuna, fomentando una experiencia positiva para los destinatarios.
- Administrar rastros de correo electrónico: Al responder o reenviar correos electrónicos, sea discreto e incluya solo información relevante, eliminando mensajes innecesarios para mantener la claridad y el enfoque.
- Evite información confidencial: Tenga cuidado al manipular información sensible o confidencial dentro de buzones compartidos y siga los protocolos establecidos para una comunicación segura.
La implementación de una etiqueta de correo electrónico adecuada mejora la imagen profesional de la organización y promueve la comunicación y la colaboración efectivas dentro del equipo.
Las organizaciones pueden garantizar que todos los miembros del equipo estén alineados en su enfoque de la comunicación por buzón compartido estableciendo expectativas claras y brindando orientación sobre las mejores prácticas en materia de correo electrónico.
Considere las siguientes estrategias para reforzar la etiqueta del correo electrónico:
- Desarrollar una guía de etiqueta de correo electrónico: Cree un documento completo que describa las pautas de etiqueta de correo electrónico específicas de su organización y las prácticas de buzón compartido.
- Proporcionar formación y coaching: Ofrecer sesiones de capacitación o talleres para educar a los miembros del equipo sobre la etiqueta adecuada del correo electrónico y su importancia para mantener un entorno de buzón compartido profesional.
- Predicar con el ejemplo: Incentive a los gerentes y líderes de equipo a modelar una etiqueta de correo electrónico apropiada, estableciendo el tono y el estándar para el resto del equipo.
Las organizaciones pueden fomentar una experiencia de buzón compartido más organizada, profesional y eficiente al priorizar e implementar consistentemente una etiqueta de correo electrónico adecuada, lo que en última instancia contribuirá a una mejor comunicación, colaboración y productividad general.
7. Supervisar y auditar la actividad del buzón compartido
Si bien los buzones compartidos están diseñados para facilitar la colaboración y agilizar la comunicación, también pueden presentar riesgos potenciales si no se supervisan y auditan adecuadamente.
Cuando varios usuarios acceden e interactúan con la misma cuenta de correo electrónico, es esencial implementar medidas para garantizar la responsabilidad, mantener la transparencia e identificar posibles problemas o violaciones de seguridad.
La supervisión y auditoría de la actividad de los buzones compartidos implica el seguimiento y registro activos de las acciones de los usuarios, las comunicaciones por correo electrónico y cualquier cambio realizado en el entorno de los buzones compartidos. Al hacerlo, las organizaciones pueden obtener numerosos beneficios, entre ellos:
- Seguridad y cumplimiento mejorados: La supervisión y la auditoría periódicas ayudan a detectar y prevenir accesos no autorizados, violaciones de datos o infracciones de las políticas y regulaciones de la organización.
- Mayor rendición de cuentas: Al rastrear las actividades de los usuarios, las organizaciones pueden garantizar que los miembros del equipo cumplan con los protocolos y pautas establecidos, lo que fomenta un sentido de responsabilidad y rendición de cuentas individual.
- Identificación de posibles problemas: Monitorear la actividad del buzón compartido puede revelar patrones o anomalías que pueden indicar problemas potenciales, como un exceso de correo electrónico, respuestas demoradas o mal manejo de información confidencial.
- Optimización de procesos: La auditoría de la actividad del buzón compartido puede proporcionar información valiosa sobre los flujos de trabajo del equipo, los patrones de comunicación y las áreas de mejora, lo que permite a las organizaciones refinar y optimizar sus procesos.
Para supervisar y auditar eficazmente la actividad del buzón compartido, tenga en cuenta las siguientes prácticas recomendadas:
- Implementar herramientas de registro y seguimiento: Utilice herramientas especializadas de monitoreo y auditoría de correo electrónico o las funciones integradas de su plataforma de correo electrónico para registrar acciones de los usuarios, comunicaciones por correo electrónico y cambios dentro del buzón compartido.
- Definir políticas y procedimientos de auditoría: Establecer políticas y procedimientos claros para realizar auditorías periódicas, especificando la frecuencia, el alcance y los criterios de revisión.
- Asignar roles de auditoría dedicados: Designar personas o equipos específicos responsables de realizar auditorías y monitorear la actividad del buzón compartido, garantizando la objetividad y el cumplimiento de los protocolos establecidos.
- Revisar permisos de usuario: Revise y audite periódicamente los permisos de usuario asignados al buzón compartido, garantizando que los niveles de acceso se alineen con los roles y responsabilidades actuales.
- Analizar registros e informes de auditoría: Revise y analice constantemente los registros e informes de auditoría para identificar posibles problemas, realizar un seguimiento de las tendencias y tomar decisiones basadas en datos para mejorar los procesos o actualizar las políticas.
- Implementar alertas y notificaciones automatizadas: Configure alertas o notificaciones automatizadas para marcar de inmediato actividades sospechosas, posibles violaciones de seguridad o desviaciones de los protocolos establecidos.
- Proporcionar capacitación y concientización: Educar a los miembros del equipo sobre la importancia de la supervisión y auditoría de buzones compartidos, reforzando las mejores prácticas y enfatizando la necesidad de transparencia y responsabilidad.
Las organizaciones pueden mejorar la seguridad, mantener el cumplimiento y fomentar una cultura de responsabilidad y transparencia implementando un proceso sólido de monitoreo y auditoría para buzones de correo compartidos.
Esta práctica recomendada protege la información confidencial, mitiga los riesgos y proporciona información valiosa para la mejora continua y la optimización de las prácticas de buzones de correo compartidos.
8. Integración con otras herramientas de colaboración
En el acelerado e interconectado entorno empresarial actual, los buzones compartidos suelen ser solo un componente de un ecosistema más amplio de herramientas y plataformas de colaboración.
Para maximizar la eficiencia y la productividad, es esencial integrar buzones compartidos con otras herramientas ampliamente utilizadas, lo que permite un flujo de información fluido y flujos de trabajo optimizados.
Al integrar buzones compartidos con otras herramientas de colaboración, las organizaciones pueden obtener numerosos beneficios, entre ellos:
- Comunicación centralizada: La integración de buzones compartidos con herramientas de gestión de proyectos, gestión de tareas o gestión de relaciones con los clientes (CRM) permite una comunicación centralizada, lo que garantiza que ninguna información pase desapercibida y que todas las partes interesadas relevantes permanezcan informadas.
- Contexto y visibilidad mejorados: Al vincular correos electrónicos a proyectos, tareas o registros de clientes específicos, los miembros del equipo obtienen un contexto valioso y visibilidad en el alcance más amplio del trabajo, lo que permite una toma de decisiones más informada y una colaboración efectiva.
- Gestión de tareas mejorada: La integración de buzones compartidos con herramientas de gestión de tareas permite la creación de tareas procesables directamente desde conversaciones de correo electrónico, lo que agiliza el flujo de trabajo y reduce el riesgo de pasar por alto elementos de seguimiento importantes.
- Aumento de la productividad: Al eliminar la necesidad de cambiar entre múltiples herramientas y plataformas, las soluciones de colaboración integradas minimizan el cambio de contexto y mejoran la productividad general.
- Mejor consistencia de datos: La integración garantiza que la información se actualice consistentemente en todas las herramientas conectadas, lo que reduce el riesgo de inconsistencias y errores de datos causados por la entrada manual o la duplicación de datos.
Al considerar la integración de buzones compartidos con otras herramientas de colaboración, las organizaciones deben explorar opciones populares como:
- Herramientas de gestión de proyectos (por ejemplo, Asana, Trello, Jira): Estas herramientas permiten a los usuarios crear tareas, asignaciones y tableros de proyectos directamente desde correos electrónicos, lo que permite una mejor organización y seguimiento de los elementos de trabajo.
- Plataformas de gestión de relaciones con el cliente (CRM) (por ejemplo, Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM): La integración de buzones compartidos con sistemas CRM garantiza que las comunicaciones e interacciones de los clientes se registren correctamente y se asocien con los registros de clientes correctos, lo que proporciona una visión integral del recorrido del cliente.
- Plataformas de almacenamiento y uso compartido de archivos (por ejemplo, Google Drive, Dropbox, OneDrive): La integración perfecta con herramientas para compartir archivos permite a los miembros del equipo acceder y compartir fácilmente documentos, archivos adjuntos u otros archivos relevantes directamente desde el entorno de buzón compartido.
- Aplicaciones de comunicación en equipo (por ejemplo, Slack, Microsoft Teams, Zoom): La integración de buzones compartidos con aplicaciones de comunicación permite recibir notificaciones, debates y colaborar en tiempo real en torno a hilos de correo electrónico o conversaciones específicas.
Para implementar con éxito estas integraciones, tenga en cuenta las siguientes prácticas recomendadas:
- Evalúe las necesidades de su equipo y las herramientas existentes: Evalúe los requisitos específicos de su equipo e identifique las herramientas de colaboración que ya están en uso para determinar las integraciones más apropiadas y valiosas.
- Involucre a las partes interesadas clave: Interactúe con miembros del equipo, gerentes y profesionales de TI para recopilar aportes y garantizar que las integraciones seleccionadas se alineen con los objetivos y flujos de trabajo de la organización.
- Proporcionar formación y documentación: Ofrecer capacitación y documentación integral para garantizar que los miembros del equipo comprendan cómo utilizar las soluciones integradas y aprovechar eficazmente todo su potencial.
- Monitorizar y perfeccionar continuamente: Revise periódicamente la eficacia de las integraciones implementadas, recopile comentarios de los usuarios y realice ajustes o mejoras según sea necesario para optimizar la experiencia colaborativa.
Al integrar buzones compartidos con otras herramientas de colaboración, las organizaciones pueden crear un espacio de trabajo digital fluido y eficiente, fomentando una mejor comunicación, coordinación y productividad entre equipos y departamentos.
9. Implementar acceso seguro y protección de datos
En el panorama digital actual, donde las violaciones de datos y las amenazas cibernéticas están en aumento, garantizar la seguridad y protección del buzón compartido es primordial.
Los buzones de correo compartidos a menudo contienen información confidencial, comunicaciones confidenciales y datos comerciales cruciales, lo que los convierte en objetivos atractivos para actores maliciosos.
Implementar medidas de seguridad sólidas y prácticas de protección de datos es una práctica recomendada fundamental para salvaguardar la valiosa información de su organización y mantener la confianza de clientes, consumidores y partes interesadas.
Acceso seguro:
- Autenticación multifactor (MFA): Implemente la autenticación multifactor para acceder a los buzones compartidos, lo que exige que los usuarios proporcionen una forma adicional de verificación además de una contraseña. Esto agrega una capa adicional de seguridad y ayuda a prevenir el acceso no autorizado.
- Controles de acceso basados en roles (RBAC): Asigne permisos de acceso en función de los roles y las responsabilidades de los usuarios dentro de la organización. Esto garantiza que solo las personas autorizadas puedan acceder a partes específicas del buzón compartido, lo que limita la posible exposición de información confidencial.
- Políticas de gestión de contraseñas: Establezca políticas de contraseñas seguras que exijan cambios periódicos de contraseñas, prohíban la reutilización de contraseñas y apliquen requisitos de complejidad. Considere implementar un sistema de gestión de contraseñas centralizado para mayor seguridad.
- Acceso remoto seguro: Si es necesario acceder a buzones compartidos de forma remota, asegúrese de que existan protocolos seguros y conexiones de red privada virtual (VPN) para protegerse contra ataques de intermediarios e intentos de acceso no autorizado.
Protección de datos:
- Cifrado de correo electrónico: Implemente soluciones de cifrado de correo electrónico para proteger la confidencialidad de las comunicaciones confidenciales dentro del buzón compartido. Esto garantiza que, incluso si se interceptan los correos electrónicos, el contenido permanecerá seguro e ilegible para terceros no autorizados.
- Prevención de pérdida de datos (DLP): Utilice herramientas DLP para monitorear y evitar la transmisión no autorizada de datos confidenciales, como información de identificación personal (PII), registros financieros o propiedad intelectual, que salgan del entorno de buzón compartido.
- Copia de seguridad y recuperación: Establezca una estrategia sólida de copia de seguridad y recuperación para los buzones de correo compartidos a fin de protegerlos contra la pérdida de datos debido a la eliminación accidental, fallas del sistema o ataques de ransomware. Las copias de seguridad periódicas deben almacenarse de forma segura y comprobarse su integridad.
- Planificación de recuperación ante desastres: Desarrolle un plan integral de recuperación ante desastres que describa los procedimientos y los pasos a seguir en caso de un incidente importante o una violación de datos que afecte al buzón compartido. Este plan debe incluir protocolos de comunicación claros, funciones y responsabilidades, y estrategias para minimizar el tiempo de inactividad y la pérdida de datos.
- Cumplimiento y auditoría: Asegúrese de que sus prácticas de buzón compartido se ajusten a las normas de cumplimiento y las regulaciones de la industria pertinentes, como GDPR, HIPAA o PCI-DSS. Implemente procesos de auditoría y monitoreo regulares para identificar y abordar posibles problemas de cumplimiento o brechas de seguridad.
Las organizaciones pueden reducir significativamente el riesgo de violaciones de datos, acceso no autorizado y posibles consecuencias legales o financieras resultantes de buzones compartidos comprometidos al priorizar el acceso seguro y las medidas de protección de datos.
Esta mejor práctica protege la información confidencial y fomenta la confianza entre clientes, consumidores y partes interesadas, reforzando el compromiso de la organización con la seguridad de la información y la privacidad de los datos.
10. Revisar y actualizar periódicamente las prácticas
En el panorama de la tecnología y las prácticas comerciales en constante evolución, es esencial reconocer que la gestión de buzones compartidos no es una tarea que se realiza una sola vez. Para garantizar que sus buzones compartidos sigan siendo eficientes, seguros y estén alineados con los objetivos de la organización, es fundamental revisar y actualizar sus prácticas y protocolos con regularidad.
La implementación de las mejores prácticas para los buzones de correo compartidos no es un proceso estático; requiere evaluación, adaptación y mejora continuas. Al revisar y actualizar periódicamente sus prácticas, puede abordar los desafíos emergentes, incorporar nuevas tecnologías o herramientas y alinearse con los requisitos comerciales cambiantes o los estándares de la industria.
A continuación se presentan algunas consideraciones clave para revisar y actualizar periódicamente sus prácticas de buzón compartido:
- Realizar auditorías y evaluaciones periódicas: Establezca un cronograma para realizar auditorías y evaluaciones integrales de sus prácticas de buzón compartido. Esto debería incluir evaluar la eficacia de los protocolos actuales, identificar áreas de mejora y recopilar comentarios de los usuarios y las partes interesadas.
- Monitorear la adopción y retroalimentación de los usuarios: Supervise continuamente el cumplimiento de las prácticas establecidas por parte de los miembros del equipo y solicite comentarios sobre áreas de dificultad, confusión o posible optimización. Esta valiosa información puede ayudar a refinar y mejorar sus estrategias de gestión de buzones compartidos.
- Manténgase actualizado sobre las tendencias y las mejores prácticas de la industria: Investigue y manténgase informado periódicamente sobre las últimas tendencias de la industria, las tecnologías emergentes y las mejores prácticas en evolución relacionadas con la administración de buzones de correo compartidos. Este conocimiento puede ayudarlo a identificar oportunidades para adoptar nuevas herramientas, técnicas o procesos que puedan mejorar las prácticas de su organización.
- Alinearse con los cambios organizacionales: A medida que su organización crece, se reestructura o cambia prioridades, revise y actualice sus prácticas de buzón compartido para garantizar la alineación con las necesidades cambiantes del negocio, los flujos de trabajo y los requisitos de comunicación.
- Revisar y actualizar políticas y documentación: Revise y actualice periódicamente las políticas, pautas y documentación de su buzón compartido para reflejar cualquier cambio en las prácticas, los procedimientos o los estándares organizacionales. Asegúrese de que estos recursos permanezcan actualizados y accesibles para todos los miembros relevantes del equipo.
- Proporcionar formación y educación continua: Implementar programas regulares de capacitación y educación para mantener a los miembros del equipo informados sobre actualizaciones en las prácticas de buzones compartidos, nuevas herramientas o integraciones y mejores prácticas para una gestión eficiente y segura de buzones.
- Mejorar continuamente las medidas de seguridad: A medida que evolucionan las amenazas cibernéticas y las preocupaciones sobre la privacidad de los datos, revise y actualice periódicamente sus medidas de seguridad y prácticas de protección de datos para mantener los más altos niveles de seguridad para sus buzones de correo compartidos.
Al adoptar una mentalidad de mejora continua y revisar y actualizar periódicamente sus prácticas de buzón compartido, puede asegurarse de que su organización se mantenga a la vanguardia, maximice la eficiencia y mantenga un entorno de comunicación seguro y colaborativo.
Esta mejor práctica fomenta la optimización continua y demuestra un compromiso con la excelencia y la adaptabilidad en un panorama empresarial en constante cambio.
Reflexiones finales
Los buzones de correo compartidos son fundamentales para la comunicación y la colaboración en equipo, pero sin una gestión adecuada, pueden desorganizarse y volverse ineficientes, lo que genera problemas como mensajes perdidos y riesgos de seguridad. Las 10 prácticas recomendadas descritas proporcionan una hoja de ruta para mantener los buzones de correo compartidos organizados y seguros.
La implementación de estas prácticas conlleva numerosos beneficios, como una mejor comunicación, una colaboración eficiente, un aumento de la productividad, una reducción de los riesgos y la garantía del cumplimiento normativo. Sin embargo, la gestión de buzones de correo compartidos requiere un esfuerzo continuo y una adaptación a las cambiantes necesidades empresariales.
Al adoptar y adaptar estas prácticas recomendadas, las organizaciones pueden capacitar a los equipos para usar buzones compartidos de manera eficaz, lo que permite una comunicación fluida, flujos de trabajo optimizados y un entorno colaborativo que impulsa el éxito.